The shocking error screen “The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)” appears in Windows when the operating system meets a critical error that it cannot recover from on its own. It appears on the screen with a blue background and white letters. This error has been affecting Windows users for numerous years. This article will go over the causes of BSOD, its impact on the Windows system, troubleshooting strategies, preventative advice, typical error codes, and data backup options.

What is Blue Screen Of Death?
The Blue Screen of Death, also known as the Stop Error or Bug Check Screen, is a blue screen that appears on the computer screen when it encounters a critical error from which it cannot recover. It usually appears with a message that describes the error details and prompts the user to restart the computer system.
What is the Impact of a BSOD on a Windows System?
Data loss is a major issue when a BSOD error occurs. A system crash, any unsaved data, or a machine shutdown, while the job is in progress, can result in potential data loss for the user.
When the BSOD error occurs, the system may not function properly and may become unstable. Frequent failures and errors can degrade system speed and dependability, resulting in an unsatisfactory user experience.
Downtime and decreased productivity are other important effects of BSOD. When a system encounters a BSOD issue, it can require troubleshooting and repair, resulting in user downtime. This can lead to decreased productivity, especially in corporate situations where time is of importance.
Users may be required to spend time resolving BSOD issues, which can disrupt their workflow and reduce productivity.
Causes of the Blue Screen Of Death (BSOD) In Windows
BSODs are usually caused by hardware drivers, software conflicts, or operating system issues. When the system encounters such errors, it automatically stops to prevent further damage and displays BSOD on the screen as a safety measure.
Windows Blue Screen of Death errors can be caused by many reasons. Including hardware and software issues as well as driver issues. Understanding the root causes can help you take appropriate steps to resolve the problem of BSOD. Here are some common causes of Blue Screen of Death in Windows :
1. Recently any Software Install Or Hardware Changes
Mostly, this problem can also happen if you have recently installed or upgraded any software or changed any hardware component. If you install software, uninstall it and if you change any hardware, remove it and check if the error is solved or not.
2. Software issues
BSOD in Windows can also be caused by software conflicts, corrupted system files, or incompatible software installation. For example, incompatible or outdated device driver installs, software updates or third-party applications can trigger the error, resulting in system instability and system crashes.
3. Hardware Issues
Faulty hardware components, RAM (random-like memory), hard drives, graphics cards, or peripherals can also cause BSOD problems. These components can be faulty or misplaced, which can cause system crashes and the dreaded blue screen.
4. Overheating for the required temperature
BSOD error can occur due to overheating of the CPU (Central Processing Unit) or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) and system shutdown. A dusty or bad cooling fan, application of bad thermal paste, or a leaking heat sink can cause overheating and the dreaded blue screen error.
5. Power Supply Issues
Power-related issues, such as surges, voltage oscillations, or an insufficient energy supply, can potentially cause the BSOD in Windows. Faulty power cables, UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), or power sockets can cause rapid interruptions in power, resulting in system crashes and the dreaded blue screen error.
6. Malware or Virus infection
Malware or virus a problem may trigger BSOD in Windows. Malicious software, such as viruses, ransomware, trojans, or rootkits, may damage system files and folders, infect other applications, and cause the screening blue screen error.
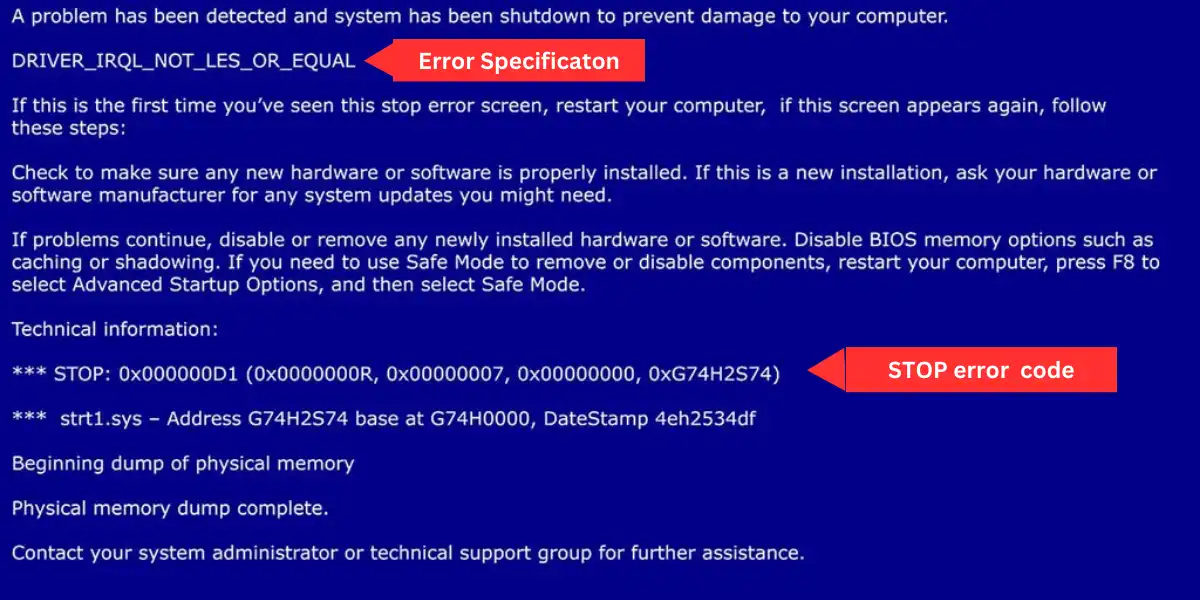
Here are some of the most common Windows stop errors, as well as their error codes and discussion.
| Stop Code | Error Specification | Error Discussion |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0000001A | MEMORY_MANAGEMENT | Errors are caused by memory management issues such as faulty RAM or memory allocation. |
| 0x0000003B | SYSTEM_SERVICE_EXCEPTION | If the system gets any error in service, and is unable to handle it, which is almost due to incompatible or outdated drivers. |
| 0x0000007B | INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE | This error takes place when the system has failed to access the bootable device, which is usually due to a problem with the hard drive or storage drivers. |
| 0x0000000A | IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL | This occurs when a kernel-mode process or driver tries to access a memory location that access is not allowed. This is often caused by incompatible drivers or faulty hardware. |
| 0x00000050 | PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED _AREA | When the system experiences a page fault in a non-paged section of memory, this is frequently caused by malfunctioning hardware, corrupt system files, or mismatched drivers. |
| 0x00000133 | DPC_WATCHDOG_VIOLATION | When a DPC (deferred procedure call) takes too long to complete, that indicates a driver or hardware device problem. |
| 0x000000EA | THREAD_STUCK_IN_DEVICE _DRIVER | When a device driver takes too long to respond, causing the system to hang. This is often related to the graphics card driver. |
| 0x000000C4 | DRIVER_VERIFIER_DETECTED _VIOLATION | When driving Verifier, a driving testing technology, discovers violations by drivers. It is frequently used for driver development and testing. |
| 0x0000007E | SYSTEM_THREAD_EXCEPTION _NOT_HANDLED | This is when a system thread encounters an exception that it cannot handle, often due to incompatible or outdated drivers. |
| 0x00000077 | KERNEL_STACK_INPAGE_ERROR | When the system experiences paging file or disc I/O issues, it is frequently caused by faulty hardware or disc issues. |
Note : Remember that many factors can cause stop codes, and solutions may differ based on the situation at hand. Examining and following proper troubleshooting processes, such as upgrading drivers, running diagnostic tools, checking hardware connections, and screening for viruses is critical. If you are not confident in your abilities, it is best to seek the advice of a knowledgeable specialist.
Solutions for Windows Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
Fixing the Blue Screen of Death in Windows can be difficult, but there are various options you can take to resolve the issue and get your system up and running again. Some possible BSOD addresses are discussed further below.
1. Update device drivers
Outdated or incompatible device drivers can cause BSOD problems in Windows. Updating device drivers to the latest version can resolve software conflicts and improve system stability. You can manually update device drivers through Device Manager or by downloading them from the manufacturer’s website and update.
2. Check software conflict
BSOD can also be caused by the installation of incompatible software. The issue may be addressed by removing or disabling recently installed or incompatible applications. To remove software that may be generating the problem, use Control Panel or a third-party uninstaller application.
3. Run System File Checker (SFC) and Disc Check.
Corrupt system files can process BSOD. Running the built-in System File Checker (SFC) tool in Windows can scan and repair damaged system files. Running Disk Check can detect and fix errors on your hard drive, both of which can help resolve BSODs.
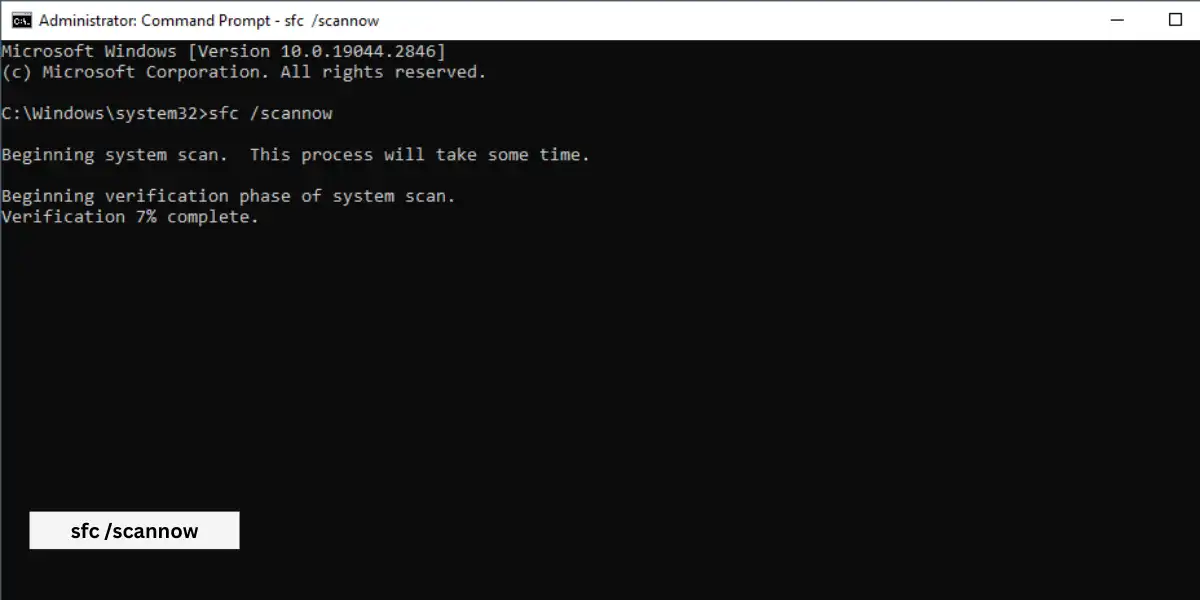
Step 1: Run System File Checker (SFC)
- Launch a Command Prompt with administrative rights. You might do this by looking for “Command Prompt” in the Start menu, right-clicking it, and selecting “Run as administrator.”
- In the command prompt window, type “sfc /scannow” without the quotes and press Enter.
- Wait for the System File Checker to scan for corrupted or missing system files and fix them. Please be patient during this process.
- After completing the process, Restart your Computer.
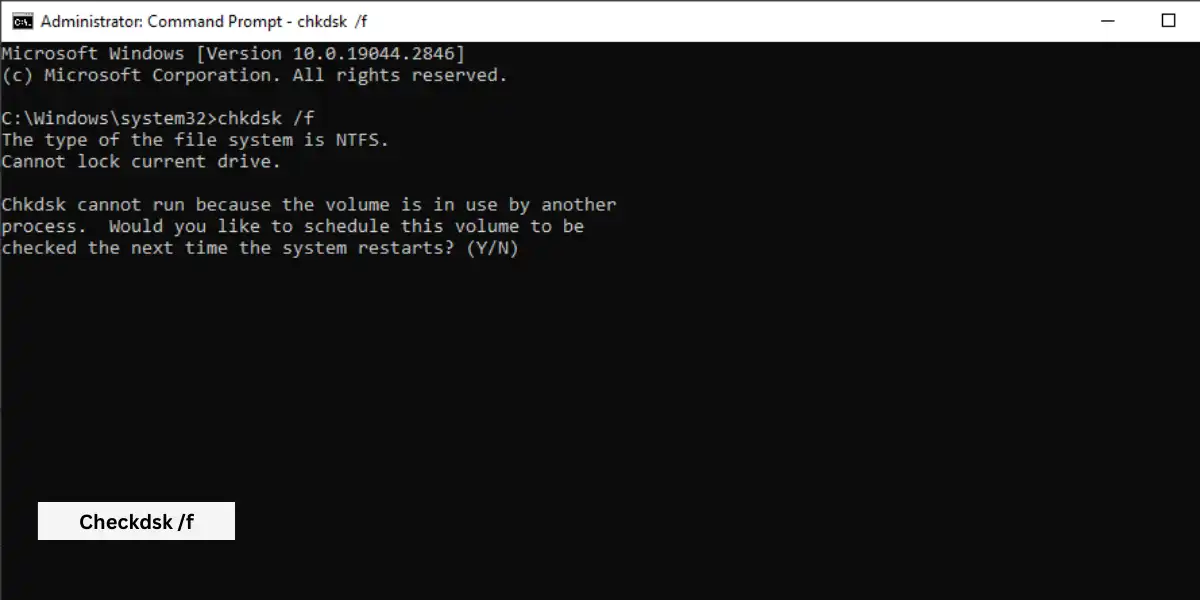
Step 2: Run Disk Check
- Open a Command Prompt with administrative privileges
- In Prompt,type “chkdsk /f” without the quotes and press Enter
- On the next restart, you will be prompted to schedule a disc check. Enter the letter “Y” for yes.
- Wait for the disk cheek complete
- When the disc check is finished, your computer will restart automatically.
4. Check for Overheating
BSOD can also occur due to CPU or GPU overheating. Check if your cooling fans are working properly, change if necessary and apply the new thermal paste and check the system.
5. Check Hardware Component
Most of the system hardware components, such as RAM, hard drive, or graphics card, can process a BSOD. Check by replacing a new component or a tested component to check which hardware is faulty. Fix the problem by having the broken one repaired and replaced with a new one or by a professional.
6. Update Bios
The BSOD might be caused by outdated or corrupt BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) firmware. Updating the BIOS to the most recent version offered by your motherboard manufacturer may assist in resolving the problem.
7. Scanning Malware or Virus Infection
Malware or virus infection can cause BSOD problems. Running a reliable antivirus or anti-malware scan can find and delete malicious software and fix the problem.
8. Check Power Supply
Power-related problems, such as insufficient power supply or leaking power cables, can cause BSOD. Check your power supply and if it is bad replace it with a new one which may help solve the BSOD problem.
9. Perform System Restore
If the BSOD started occurring after a recent software or driver installation, restoring the system to a previous stable state may help resolve the issue.
10. Install Fresh Operating System
Even if the BSOD is not fixed, a fresh installation of the system could help solve the problem.
11. Seek Professional Help
If unable to resolve the BSOD problem on your own, seeking professional help from a computer technician support may be a good option. Cheek Common Pc Solution Error.
Conclusion
Finally, the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a frustrating mistake that can occur on Windows PCs, signifying a major problem that demands rapid attention. Understanding the causes, troubleshooting strategies, and avoidance suggestions will assist users in handling BSOD errors effectively and reducing their impact on system performance and productivity.
FAQs
What causes blue screen BSOD in Windows?
Blue Screen of Death is usually caused by incompatible software conflicts, hardware issues, overheating, memory issues, malware, and virus infections. Failure to properly integrate driver updates with the rest of your system can cause a blue screen of death
How do I fix Blue Screen of Death on Windows?
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a serious error that occurs in Windows operating systems. To fix this you can follow some simple working steps:
1. Restart your Computer: Sometimes a simple restart can resolve the Issue.
2. Undo Recent Changes: If you recently made any changes to your system settings, hardware changes, software installations, or updates, try undoing them to see if the BSOD disappears. You can use System Restore to back to your system’s previous state.
3. Update Device Driver: Outdated or Incompatible device driver can cause a BSOD error.
4. Scan for Malware: Malware infections can corrupt system files and cause BSOD errors.
5. Hardware Issues: Faulty Hardware can cause this Error
Can RAM cause a blue screen BSOD?
Mostly bad memory (RAM), corrupted hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD), motherboard, overheating processor, or defective power supply unit (SMPS) can all be at fault for blue screen crashes.
Can I lose my data due to the BSOD?
Yes, BSOD can result in the loss of unsaved data as the system needs to be restarted. It is very important to save your work regularly to avoid possible data loss.
Can I fix a BSOD error on my own?
BSOD errors occur for various reasons. It may be possible to fix it yourself using troubleshooting techniques like checking device drivers, booting into safe mode, running system diagnostics, and restoring the system to a previous restore point. However, in some cases, professional help may be required.